C Programming Interview Preparation: Top 50 Questions and Answers

C programming interviews assess fundamental computer science knowledge through questions about pointers, memory management, data structures, and algorithmic problem-solving with hands-on coding [web:344][web:352]. This comprehensive guide presents 50 essential interview questions with complete code examples, detailed explanations, and common pitfalls, organized into logical categories covering pointers and memory, data structures implementation, strings and arrays, algorithms, and advanced C concepts [web:354][web:355]. Each question includes working code demonstrating the concept, making this guide practical for interview preparation at companies ranging from startups to tech giants like Google, Amazon, and Microsoft.
Mastering these 50 questions requires understanding low-level memory operations, implementing data structures from scratch using structures and pointers, analyzing time and space complexity, and debugging common issues like segmentation faults and memory leaks [web:343][web:358]. By studying these questions systematically with hands-on practice, candidates develop the deep understanding and problem-solving abilities that distinguish strong programmers in technical interviews.
Pointers and Memory Management (Q1-Q15)
Pointer questions dominate C interviews because they test understanding of memory architecture and low-level programming [web:343][web:358]. These 15 questions cover pointer fundamentals, dynamic memory allocation, pointer arithmetic, and common pitfalls like dangling pointers and memory leaks.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// ============================================
// Q1: What is a pointer? Demonstrate basic pointer operations.
// ============================================
void question1_pointerBasics() {
int x = 10;
int *ptr = &x; // ptr stores address of x
printf("Q1: Pointer Basics\n");
printf("Value of x: %d\n", x);
printf("Address of x: %p\n", (void*)&x);
printf("Value of ptr (address): %p\n", (void*)ptr);
printf("Value at address (*ptr): %d\n", *ptr);
*ptr = 20; // Modify x through pointer
printf("After *ptr = 20, x = %d\n\n", x);
}
// ============================================
// Q2: What is a null pointer? How do you check for it?
// ============================================
void question2_nullPointer() {
int *ptr = NULL;
printf("Q2: Null Pointer\n");
if (ptr == NULL) {
printf("Pointer is NULL - safe to check before dereferencing\n");
}
// Always check before using malloc result
ptr = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int));
if (ptr == NULL) {
printf("Memory allocation failed\n");
return;
}
*ptr = 100;
printf("Successfully allocated and assigned: %d\n", *ptr);
free(ptr);
ptr = NULL; // Good practice: set to NULL after free
printf("\n");
}
// ============================================
// Q3: What is a dangling pointer? Demonstrate the problem.
// ============================================
void question3_danglingPointer() {
printf("Q3: Dangling Pointer\n");
int *ptr = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int));
*ptr = 50;
printf("Value: %d\n", *ptr);
free(ptr);
// ptr is now dangling - points to freed memory
// Accessing *ptr here causes undefined behavior!
ptr = NULL; // Solution: set to NULL
printf("Set pointer to NULL after free to prevent dangling\n\n");
}
// ============================================
// Q4: Explain pointer arithmetic with arrays.
// ============================================
void question4_pointerArithmetic() {
printf("Q4: Pointer Arithmetic\n");
int arr[] = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50};
int *ptr = arr; // Points to first element
printf("Array elements using pointer arithmetic:\n");
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
printf("*(ptr + %d) = %d at address %p\n",
i, *(ptr + i), (void*)(ptr + i));
}
printf("\nptr + 1 moves by %lu bytes (sizeof(int))\n\n", sizeof(int));
}
// ============================================
// Q5: What is void pointer? Demonstrate its use.
// ============================================
void question5_voidPointer() {
printf("Q5: Void Pointer\n");
int num = 42;
float pi = 3.14;
void *vptr;
// Void pointer can point to any type
vptr = #
printf("Integer via void*: %d\n", *(int*)vptr);
vptr = π
printf("Float via void*: %.2f\n", *(float*)vptr);
printf("Note: Must cast before dereferencing\n\n");
}
// ============================================
// Q6: Explain pointer to pointer (double pointer).
// ============================================
void modifyPointer(int **pp) {
static int value = 999;
*pp = &value; // Modify the pointer itself
}
void question6_pointerToPointer() {
printf("Q6: Pointer to Pointer\n");
int x = 10;
int *ptr = &x;
int **pp = &ptr;
printf("Value of x: %d\n", x);
printf("*ptr: %d\n", *ptr);
printf("**pp: %d\n", **pp);
modifyPointer(&ptr);
printf("After modifyPointer, *ptr: %d\n\n", *ptr);
}
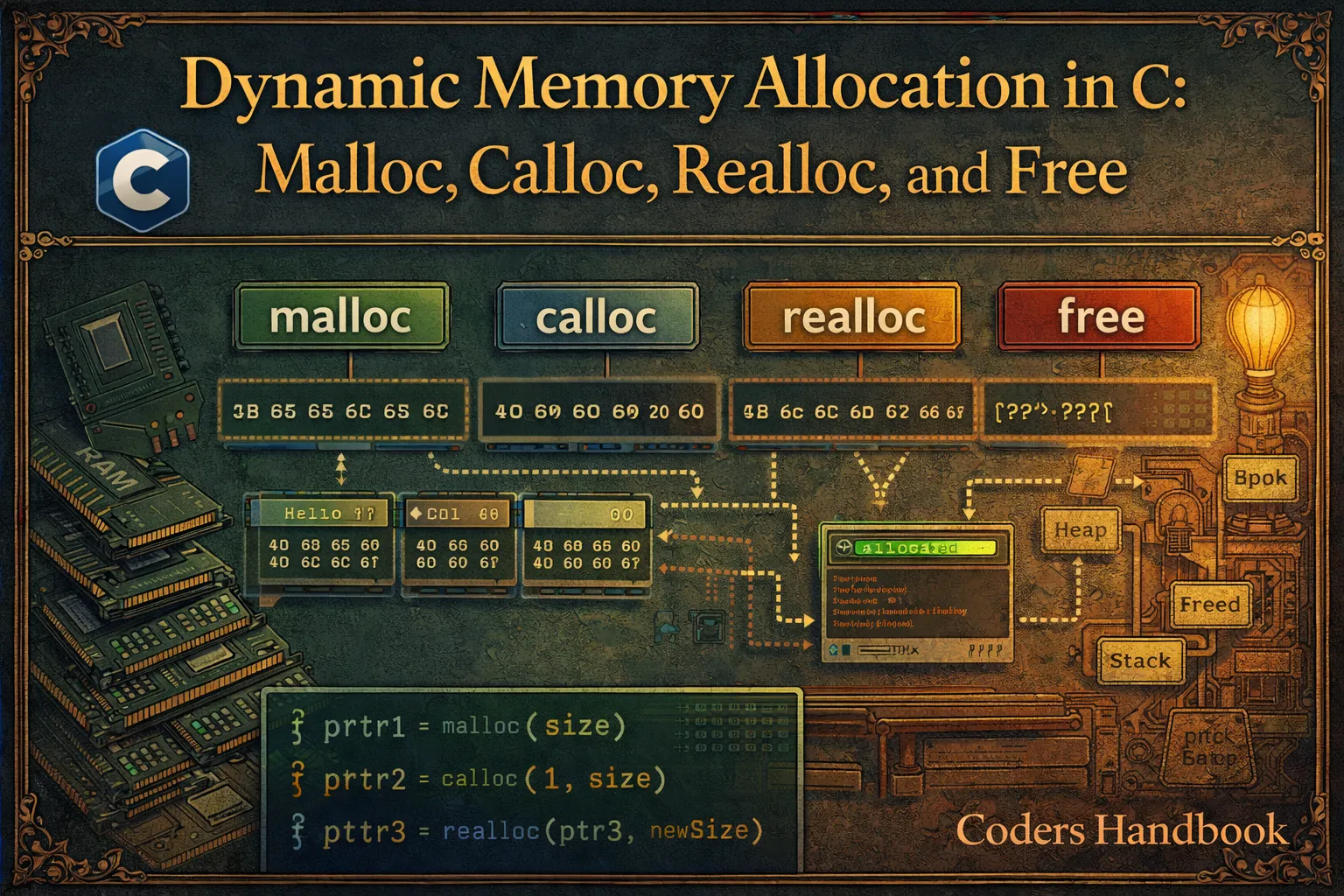
// ============================================
// Q7: malloc vs calloc - demonstrate the difference.
// ============================================
void question7_mallocVsCalloc() {
printf("Q7: malloc vs calloc\n");
int *arr1 = (int*)malloc(5 * sizeof(int));
int *arr2 = (int*)calloc(5, sizeof(int));
printf("malloc (uninitialized): ");
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
printf("%d ", arr1[i]); // Garbage values
}
printf("\ncalloc (zero-initialized): ");
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
printf("%d ", arr2[i]); // All zeros
}
free(arr1);
free(arr2);
printf("\n\n");
}
// ============================================
// Q8: How does realloc work? Demonstrate resizing.
// ============================================
void question8_realloc() {
printf("Q8: realloc\n");
int *arr = (int*)malloc(3 * sizeof(int));
if (arr == NULL) return;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
arr[i] = i * 10;
}
printf("Original array (size 3): ");
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
}
// Resize to 6 elements
int *temp = (int*)realloc(arr, 6 * sizeof(int));
if (temp != NULL) {
arr = temp;
for (int i = 3; i < 6; i++) {
arr[i] = i * 10;
}
}
printf("\nResized array (size 6): ");
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
}
free(arr);
printf("\n\n");
}
// ============================================
// Q9: Implement pass by reference using pointers.
// ============================================
void swap(int *a, int *b) {
int temp = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = temp;
}
void question9_passByReference() {
printf("Q9: Pass by Reference (Swap)\n");
int x = 5, y = 10;
printf("Before swap: x=%d, y=%d\n", x, y);
swap(&x, &y);
printf("After swap: x=%d, y=%d\n\n", x, y);
}
// ============================================
// Q10: What is a function pointer? Demonstrate callback.
// ============================================
int add(int a, int b) { return a + b; }
int multiply(int a, int b) { return a * b; }
void calculate(int x, int y, int (*operation)(int, int)) {
printf("Result: %d\n", operation(x, y));
}
void question10_functionPointer() {
printf("Q10: Function Pointer\n");
int (*fp)(int, int);
fp = add;
printf("Using add: ");
calculate(5, 3, fp);
fp = multiply;
printf("Using multiply: ");
calculate(5, 3, fp);
printf("\n");
}
// ============================================
// Q11: Demonstrate memory leak detection pattern.
// ============================================
void question11_memoryLeak() {
printf("Q11: Memory Leak Prevention\n");
// Bad: memory leak
int *leak = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int));
*leak = 100;
leak = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)); // Lost reference!
// Good: free before reassigning
int *ptr = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int));
*ptr = 200;
free(ptr);
ptr = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int));
*ptr = 300;
free(ptr);
printf("Always free before losing pointer reference\n\n");
}
// ============================================
// Q12: Stack vs Heap memory allocation.
// ============================================
void question12_stackVsHeap() {
printf("Q12: Stack vs Heap\n");
// Stack allocation
int stack_var = 100;
printf("Stack variable: %d at %p\n", stack_var, (void*)&stack_var);
// Heap allocation
int *heap_var = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int));
*heap_var = 200;
printf("Heap variable: %d at %p\n", *heap_var, (void*)heap_var);
printf("Stack: automatic, fast, limited size\n");
printf("Heap: manual, flexible, larger\n");
free(heap_var);
printf("\n");
}
// ============================================
// Q13: Demonstrate array of pointers.
// ============================================
void question13_arrayOfPointers() {
printf("Q13: Array of Pointers\n");
char *names[] = {"Alice", "Bob", "Charlie"};
printf("Names array:\n");
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
printf("%d: %s\n", i, names[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
// ============================================
// Q14: Pointer to array vs array of pointers.
// ============================================
void question14_pointerToArray() {
printf("Q14: Pointer to Array\n");
int arr[5] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
int (*ptr)[5] = &arr; // Pointer to entire array
printf("Array elements via pointer to array:\n");
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
printf("%d ", (*ptr)[i]);
}
printf("\n\n");
}
// ============================================
// Q15: Dynamic 2D array allocation.
// ============================================
void question15_dynamic2DArray() {
printf("Q15: Dynamic 2D Array\n");
int rows = 3, cols = 4;
// Allocate array of pointers
int **matrix = (int**)malloc(rows * sizeof(int*));
// Allocate each row
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
matrix[i] = (int*)malloc(cols * sizeof(int));
}
// Fill matrix
int value = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++) {
matrix[i][j] = value++;
}
}
// Print matrix
printf("3x4 matrix:\n");
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++) {
printf("%2d ", matrix[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
// Free memory
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
free(matrix[i]);
}
free(matrix);
printf("\n");
}
int main() {
printf("=== C Interview Questions: Pointers & Memory ===\n\n");
question1_pointerBasics();
question2_nullPointer();
question3_danglingPointer();
question4_pointerArithmetic();
question5_voidPointer();
question6_pointerToPointer();
question7_mallocVsCalloc();
question8_realloc();
question9_passByReference();
question10_functionPointer();
question11_memoryLeak();
question12_stackVsHeap();
question13_arrayOfPointers();
question14_pointerToArray();
question15_dynamic2DArray();
return 0;
}Strings and Arrays (Q16-Q25)
String and array manipulation tests knowledge of C's null-terminated strings, standard library functions, and efficient algorithms [web:352][web:354]. These 10 questions cover string operations, array searching, sorting, and common interview problems like palindrome checking and duplicate removal.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
// ============================================
// Q16: Reverse a string in place.
// ============================================
void reverseString(char *str) {
int len = strlen(str);
for (int i = 0; i < len / 2; i++) {
char temp = str[i];
str[i] = str[len - 1 - i];
str[len - 1 - i] = temp;
}
}
void question16_reverseString() {
printf("Q16: Reverse String\n");
char str[] = "Hello World";
printf("Original: %s\n", str);
reverseString(str);
printf("Reversed: %s\n\n", str);
}
// ============================================
// Q17: Check if string is palindrome.
// ============================================
bool isPalindrome(char *str) {
int len = strlen(str);
for (int i = 0; i < len / 2; i++) {
if (str[i] != str[len - 1 - i]) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
void question17_palindrome() {
printf("Q17: Palindrome Check\n");
char *test1 = "racecar";
char *test2 = "hello";
printf("%s is %s\n", test1, isPalindrome(test1) ? "palindrome" : "not palindrome");
printf("%s is %s\n\n", test2, isPalindrome(test2) ? "palindrome" : "not palindrome");
}
// ============================================
// Q18: Find length of string without strlen.
// ============================================
int stringLength(char *str) {
int len = 0;
while (str[len] != '\0') {
len++;
}
return len;
}
void question18_stringLength() {
printf("Q18: String Length Without strlen\n");
char *str = "Programming";
printf("String: %s\n", str);
printf("Length: %d\n\n", stringLength(str));
}
// ============================================
// Q19: Count vowels in a string.
// ============================================
int countVowels(char *str) {
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; str[i] != '\0'; i++) {
char c = str[i];
if (c == 'a' || c == 'e' || c == 'i' || c == 'o' || c == 'u' ||
c == 'A' || c == 'E' || c == 'I' || c == 'O' || c == 'U') {
count++;
}
}
return count;
}
void question19_countVowels() {
printf("Q19: Count Vowels\n");
char *str = "Hello World";
printf("String: %s\n", str);
printf("Vowel count: %d\n\n", countVowels(str));
}
// ============================================
// Q20: Remove duplicate characters from string.
// ============================================
void removeDuplicates(char *str) {
int len = strlen(str);
int tail = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < len; i++) {
int j;
for (j = 0; j < tail; j++) {
if (str[i] == str[j]) {
break;
}
}
if (j == tail) {
str[tail++] = str[i];
}
}
str[tail] = '\0';
}
void question20_removeDuplicates() {
printf("Q20: Remove Duplicate Characters\n");
char str[] = "programming";
printf("Original: %s\n", str);
removeDuplicates(str);
printf("After removing duplicates: %s\n\n", str);
}
// ============================================
// Q21: Find largest element in array.
// ============================================
int findLargest(int arr[], int n) {
int max = arr[0];
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (arr[i] > max) {
max = arr[i];
}
}
return max;
}
void question21_largestElement() {
printf("Q21: Find Largest Element\n");
int arr[] = {12, 45, 67, 23, 89, 34};
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
printf("Array: ");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
}
printf("\nLargest: %d\n\n", findLargest(arr, n));
}
// ============================================
// Q22: Remove duplicates from sorted array.
// ============================================
int removeDuplicatesSorted(int arr[], int n) {
if (n == 0) return 0;
int j = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (arr[i] != arr[j]) {
j++;
arr[j] = arr[i];
}
}
return j + 1;
}
void question22_removeDuplicatesArray() {
printf("Q22: Remove Duplicates from Sorted Array\n");
int arr[] = {1, 1, 2, 2, 3, 4, 4, 5};
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
printf("Original: ");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
}
int newLen = removeDuplicatesSorted(arr, n);
printf("\nAfter removing duplicates: ");
for (int i = 0; i < newLen; i++) {
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
}
printf("\n\n");
}
// ============================================
// Q23: Rotate array by k positions.
// ============================================
void reverseArray(int arr[], int start, int end) {
while (start < end) {
int temp = arr[start];
arr[start] = arr[end];
arr[end] = temp;
start++;
end--;
}
}
void rotateArray(int arr[], int n, int k) {
k = k % n;
reverseArray(arr, 0, n - 1);
reverseArray(arr, 0, k - 1);
reverseArray(arr, k, n - 1);
}
void question23_rotateArray() {
printf("Q23: Rotate Array\n");
int arr[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
printf("Original: ");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
}
rotateArray(arr, n, 2);
printf("\nAfter rotating by 2: ");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
}
printf("\n\n");
}
// ============================================
// Q24: Find pair with given sum (sorted array).
// ============================================
bool findPairWithSum(int arr[], int n, int target) {
int left = 0, right = n - 1;
while (left < right) {
int sum = arr[left] + arr[right];
if (sum == target) {
printf("Pair found: %d + %d = %d\n", arr[left], arr[right], target);
return true;
} else if (sum < target) {
left++;
} else {
right--;
}
}
return false;
}
void question24_findPair() {
printf("Q24: Find Pair with Sum (Two Pointer)\n");
int arr[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6};
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
int target = 9;
printf("Array: ");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
}
printf("\nTarget sum: %d\n", target);
if (!findPairWithSum(arr, n, target)) {
printf("No pair found\n");
}
printf("\n");
}
// ============================================
// Q25: Merge two sorted arrays.
// ============================================
void mergeSortedArrays(int arr1[], int n1, int arr2[], int n2, int result[]) {
int i = 0, j = 0, k = 0;
while (i < n1 && j < n2) {
if (arr1[i] <= arr2[j]) {
result[k++] = arr1[i++];
} else {
result[k++] = arr2[j++];
}
}
while (i < n1) result[k++] = arr1[i++];
while (j < n2) result[k++] = arr2[j++];
}
void question25_mergeArrays() {
printf("Q25: Merge Two Sorted Arrays\n");
int arr1[] = {1, 3, 5, 7};
int arr2[] = {2, 4, 6, 8};
int n1 = 4, n2 = 4;
int result[8];
mergeSortedArrays(arr1, n1, arr2, n2, result);
printf("Merged array: ");
for (int i = 0; i < n1 + n2; i++) {
printf("%d ", result[i]);
}
printf("\n\n");
}
int main() {
printf("=== C Interview Questions: Strings & Arrays ===\n\n");
question16_reverseString();
question17_palindrome();
question18_stringLength();
question19_countVowels();
question20_removeDuplicates();
question21_largestElement();
question22_removeDuplicatesArray();
question23_rotateArray();
question24_findPair();
question25_mergeArrays();
return 0;
}Data Structures (Q26-Q35)
Implementing data structures from scratch tests understanding of memory management, pointers, and algorithmic thinking [web:354][web:359]. These 10 questions cover linked lists, stacks, queues, and fundamental operations including insertion, deletion, searching, and traversal.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
// ============================================
// Q26: Implement a singly linked list with basic operations.
// ============================================
typedef struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* next;
} Node;
Node* createNode(int data) {
Node* newNode = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
newNode->data = data;
newNode->next = NULL;
return newNode;
}
void insertAtBeginning(Node** head, int data) {
Node* newNode = createNode(data);
newNode->next = *head;
*head = newNode;
}
void displayList(Node* head) {
Node* current = head;
while (current != NULL) {
printf("%d -> ", current->data);
current = current->next;
}
printf("NULL\n");
}
void question26_linkedList() {
printf("Q26: Singly Linked List\n");
Node* head = NULL;
insertAtBeginning(&head, 30);
insertAtBeginning(&head, 20);
insertAtBeginning(&head, 10);
printf("Linked List: ");
displayList(head);
printf("\n");
}
// ============================================
// Q27: Reverse a linked list.
// ============================================
Node* reverseList(Node* head) {
Node* prev = NULL;
Node* current = head;
Node* next = NULL;
while (current != NULL) {
next = current->next;
current->next = prev;
prev = current;
current = next;
}
return prev;
}
void question27_reverseList() {
printf("Q27: Reverse Linked List\n");
Node* head = NULL;
insertAtBeginning(&head, 30);
insertAtBeginning(&head, 20);
insertAtBeginning(&head, 10);
printf("Original: ");
displayList(head);
head = reverseList(head);
printf("Reversed: ");
displayList(head);
printf("\n");
}
// ============================================
// Q28: Detect loop in linked list (Floyd's algorithm).
// ============================================
bool detectLoop(Node* head) {
Node* slow = head;
Node* fast = head;
while (fast != NULL && fast->next != NULL) {
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
if (slow == fast) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
void question28_detectLoop() {
printf("Q28: Detect Loop in Linked List\n");
Node* head = createNode(10);
head->next = createNode(20);
head->next->next = createNode(30);
head->next->next->next = createNode(40);
printf("List without loop: %s\n", detectLoop(head) ? "Loop found" : "No loop");
// Create loop
head->next->next->next->next = head->next;
printf("List with loop: %s\n\n", detectLoop(head) ? "Loop found" : "No loop");
}
// ============================================
// Q29: Find middle element of linked list.
// ============================================
int findMiddle(Node* head) {
Node* slow = head;
Node* fast = head;
while (fast != NULL && fast->next != NULL) {
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
}
return slow->data;
}
void question29_findMiddle() {
printf("Q29: Find Middle Element\n");
Node* head = NULL;
for (int i = 50; i >= 10; i -= 10) {
insertAtBeginning(&head, i);
}
printf("List: ");
displayList(head);
printf("Middle element: %d\n\n", findMiddle(head));
}
// ============================================
// Q30: Delete a node from linked list.
// ============================================
void deleteNode(Node** head, int key) {
Node* temp = *head;
Node* prev = NULL;
if (temp != NULL && temp->data == key) {
*head = temp->next;
free(temp);
return;
}
while (temp != NULL && temp->data != key) {
prev = temp;
temp = temp->next;
}
if (temp == NULL) return;
prev->next = temp->next;
free(temp);
}
void question30_deleteNode() {
printf("Q30: Delete Node from Linked List\n");
Node* head = NULL;
insertAtBeginning(&head, 40);
insertAtBeginning(&head, 30);
insertAtBeginning(&head, 20);
insertAtBeginning(&head, 10);
printf("Before deletion: ");
displayList(head);
deleteNode(&head, 30);
printf("After deleting 30: ");
displayList(head);
printf("\n");
}
// ============================================
// Q31: Implement stack using array.
// ============================================
#define MAX_SIZE 100
typedef struct {
int items[MAX_SIZE];
int top;
} Stack;
void initStack(Stack* s) {
s->top = -1;
}
bool isEmpty(Stack* s) {
return s->top == -1;
}
bool isFull(Stack* s) {
return s->top == MAX_SIZE - 1;
}
void push(Stack* s, int value) {
if (isFull(s)) {
printf("Stack overflow\n");
return;
}
s->items[++(s->top)] = value;
}
int pop(Stack* s) {
if (isEmpty(s)) {
printf("Stack underflow\n");
return -1;
}
return s->items[(s->top)--];
}
int peek(Stack* s) {
if (isEmpty(s)) return -1;
return s->items[s->top];
}
void question31_stackArray() {
printf("Q31: Stack Using Array\n");
Stack stack;
initStack(&stack);
push(&stack, 10);
push(&stack, 20);
push(&stack, 30);
printf("Peek: %d\n", peek(&stack));
printf("Pop: %d\n", pop(&stack));
printf("Peek: %d\n\n", peek(&stack));
}
// ============================================
// Q32: Check balanced parentheses using stack.
// ============================================
bool isBalanced(char* expr) {
Stack s;
initStack(&s);
for (int i = 0; expr[i] != '\0'; i++) {
if (expr[i] == '(' || expr[i] == '[' || expr[i] == '{') {
push(&s, expr[i]);
} else if (expr[i] == ')' || expr[i] == ']' || expr[i] == '}') {
if (isEmpty(&s)) return false;
char top = pop(&s);
if ((expr[i] == ')' && top != '(') ||
(expr[i] == ']' && top != '[') ||
(expr[i] == '}' && top != '{')) {
return false;
}
}
}
return isEmpty(&s);
}
void question32_balancedParentheses() {
printf("Q32: Balanced Parentheses\n");
char *expr1 = "{[()]}";
char *expr2 = "{[(])}";
printf("%s is %s\n", expr1, isBalanced(expr1) ? "balanced" : "not balanced");
printf("%s is %s\n\n", expr2, isBalanced(expr2) ? "balanced" : "not balanced");
}
// ============================================
// Q33: Implement queue using linked list.
// ============================================
typedef struct QueueNode {
int data;
struct QueueNode* next;
} QueueNode;
typedef struct {
QueueNode* front;
QueueNode* rear;
} Queue;
void initQueue(Queue* q) {
q->front = q->rear = NULL;
}
void enqueue(Queue* q, int value) {
QueueNode* newNode = (QueueNode*)malloc(sizeof(QueueNode));
newNode->data = value;
newNode->next = NULL;
if (q->rear == NULL) {
q->front = q->rear = newNode;
return;
}
q->rear->next = newNode;
q->rear = newNode;
}
int dequeue(Queue* q) {
if (q->front == NULL) {
printf("Queue is empty\n");
return -1;
}
QueueNode* temp = q->front;
int data = temp->data;
q->front = q->front->next;
if (q->front == NULL) q->rear = NULL;
free(temp);
return data;
}
void question33_queueLinkedList() {
printf("Q33: Queue Using Linked List\n");
Queue queue;
initQueue(&queue);
enqueue(&queue, 100);
enqueue(&queue, 200);
enqueue(&queue, 300);
printf("Dequeue: %d\n", dequeue(&queue));
printf("Dequeue: %d\n\n", dequeue(&queue));
}
// ============================================
// Q34: Find nth node from end of linked list.
// ============================================
int nthFromEnd(Node* head, int n) {
Node* main_ptr = head;
Node* ref_ptr = head;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (ref_ptr == NULL) return -1;
ref_ptr = ref_ptr->next;
}
while (ref_ptr != NULL) {
main_ptr = main_ptr->next;
ref_ptr = ref_ptr->next;
}
return main_ptr->data;
}
void question34_nthFromEnd() {
printf("Q34: Nth Node from End\n");
Node* head = NULL;
for (int i = 50; i >= 10; i -= 10) {
insertAtBeginning(&head, i);
}
printf("List: ");
displayList(head);
printf("3rd node from end: %d\n\n", nthFromEnd(head, 3));
}
// ============================================
// Q35: Check if linked list is palindrome.
// ============================================
bool isPalindromeList(Node* head) {
if (head == NULL) return true;
// Find middle
Node* slow = head;
Node* fast = head;
Stack s;
initStack(&s);
while (fast != NULL && fast->next != NULL) {
push(&s, slow->data);
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
}
// Odd number of elements
if (fast != NULL) {
slow = slow->next;
}
// Compare second half with stack
while (slow != NULL) {
if (pop(&s) != slow->data) {
return false;
}
slow = slow->next;
}
return true;
}
void question35_palindromeList() {
printf("Q35: Check Palindrome Linked List\n");
Node* head = NULL;
insertAtBeginning(&head, 10);
insertAtBeginning(&head, 20);
insertAtBeginning(&head, 20);
insertAtBeginning(&head, 10);
printf("List: ");
displayList(head);
printf("Is palindrome: %s\n\n", isPalindromeList(head) ? "Yes" : "No");
}
int main() {
printf("=== C Interview Questions: Data Structures ===\n\n");
question26_linkedList();
question27_reverseList();
question28_detectLoop();
question29_findMiddle();
question30_deleteNode();
question31_stackArray();
question32_balancedParentheses();
question33_queueLinkedList();
question34_nthFromEnd();
question35_palindromeList();
return 0;
}Sorting and Searching (Q36-Q42)
Algorithm questions evaluate understanding of time complexity, space complexity, and ability to implement efficient solutions [web:352][web:354]. These 7 questions cover binary search, bubble sort, selection sort, insertion sort, quick sort, merge sort, and linear search with complexity analysis.
#include <stdio.h>
void printArray(int arr[], int n) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
// ============================================
// Q36: Binary Search (O(log n)).
// ============================================
int binarySearch(int arr[], int n, int target) {
int left = 0, right = n - 1;
while (left <= right) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if (arr[mid] == target) {
return mid;
} else if (arr[mid] < target) {
left = mid + 1;
} else {
right = mid - 1;
}
}
return -1;
}
void question36_binarySearch() {
printf("Q36: Binary Search\n");
int arr[] = {2, 5, 8, 12, 16, 23, 38, 56, 72, 91};
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
int target = 23;
printf("Array: ");
printArray(arr, n);
int index = binarySearch(arr, n, target);
if (index != -1) {
printf("%d found at index %d\n", target, index);
} else {
printf("%d not found\n", target);
}
printf("Time: O(log n), Space: O(1)\n\n");
}
// ============================================
// Q37: Bubble Sort (O(n²)).
// ============================================
void bubbleSort(int arr[], int n) {
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
int swapped = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < n - i - 1; j++) {
if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1]) {
int temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j + 1];
arr[j + 1] = temp;
swapped = 1;
}
}
if (!swapped) break;
}
}
void question37_bubbleSort() {
printf("Q37: Bubble Sort\n");
int arr[] = {64, 34, 25, 12, 22, 11, 90};
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
printf("Before: ");
printArray(arr, n);
bubbleSort(arr, n);
printf("After: ");
printArray(arr, n);
printf("Time: O(n²), Space: O(1)\n\n");
}
// ============================================
// Q38: Selection Sort (O(n²)).
// ============================================
void selectionSort(int arr[], int n) {
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
int min_idx = i;
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++) {
if (arr[j] < arr[min_idx]) {
min_idx = j;
}
}
if (min_idx != i) {
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[min_idx];
arr[min_idx] = temp;
}
}
}
void question38_selectionSort() {
printf("Q38: Selection Sort\n");
int arr[] = {64, 25, 12, 22, 11};
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
printf("Before: ");
printArray(arr, n);
selectionSort(arr, n);
printf("After: ");
printArray(arr, n);
printf("Time: O(n²), Space: O(1)\n\n");
}
// ============================================
// Q39: Insertion Sort (O(n²)).
// ============================================
void insertionSort(int arr[], int n) {
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
int key = arr[i];
int j = i - 1;
while (j >= 0 && arr[j] > key) {
arr[j + 1] = arr[j];
j--;
}
arr[j + 1] = key;
}
}
void question39_insertionSort() {
printf("Q39: Insertion Sort\n");
int arr[] = {12, 11, 13, 5, 6};
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
printf("Before: ");
printArray(arr, n);
insertionSort(arr, n);
printf("After: ");
printArray(arr, n);
printf("Time: O(n²) worst, O(n) best, Space: O(1)\n\n");
}
// ============================================
// Q40: Quick Sort (O(n log n) average).
// ============================================
int partition(int arr[], int low, int high) {
int pivot = arr[high];
int i = low - 1;
for (int j = low; j < high; j++) {
if (arr[j] < pivot) {
i++;
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
}
}
int temp = arr[i + 1];
arr[i + 1] = arr[high];
arr[high] = temp;
return i + 1;
}
void quickSort(int arr[], int low, int high) {
if (low < high) {
int pi = partition(arr, low, high);
quickSort(arr, low, pi - 1);
quickSort(arr, pi + 1, high);
}
}
void question40_quickSort() {
printf("Q40: Quick Sort\n");
int arr[] = {10, 7, 8, 9, 1, 5};
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
printf("Before: ");
printArray(arr, n);
quickSort(arr, 0, n - 1);
printf("After: ");
printArray(arr, n);
printf("Time: O(n log n) avg, O(n²) worst, Space: O(log n)\n\n");
}
// ============================================
// Q41: Merge Sort (O(n log n)).
// ============================================
void merge(int arr[], int left, int mid, int right) {
int n1 = mid - left + 1;
int n2 = right - mid;
int L[n1], R[n2];
for (int i = 0; i < n1; i++)
L[i] = arr[left + i];
for (int j = 0; j < n2; j++)
R[j] = arr[mid + 1 + j];
int i = 0, j = 0, k = left;
while (i < n1 && j < n2) {
if (L[i] <= R[j]) {
arr[k++] = L[i++];
} else {
arr[k++] = R[j++];
}
}
while (i < n1) arr[k++] = L[i++];
while (j < n2) arr[k++] = R[j++];
}
void mergeSort(int arr[], int left, int right) {
if (left < right) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
mergeSort(arr, left, mid);
mergeSort(arr, mid + 1, right);
merge(arr, left, mid, right);
}
}
void question41_mergeSort() {
printf("Q41: Merge Sort\n");
int arr[] = {12, 11, 13, 5, 6, 7};
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
printf("Before: ");
printArray(arr, n);
mergeSort(arr, 0, n - 1);
printf("After: ");
printArray(arr, n);
printf("Time: O(n log n), Space: O(n)\n\n");
}
// ============================================
// Q42: Linear Search (O(n)).
// ============================================
int linearSearch(int arr[], int n, int target) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (arr[i] == target) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
void question42_linearSearch() {
printf("Q42: Linear Search\n");
int arr[] = {64, 34, 25, 12, 22, 11, 90};
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
int target = 22;
printf("Array: ");
printArray(arr, n);
int index = linearSearch(arr, n, target);
if (index != -1) {
printf("%d found at index %d\n", target, index);
} else {
printf("%d not found\n", target);
}
printf("Time: O(n), Space: O(1)\n\n");
}
int main() {
printf("=== C Interview Questions: Sorting & Searching ===\n\n");
question36_binarySearch();
question37_bubbleSort();
question38_selectionSort();
question39_insertionSort();
question40_quickSort();
question41_mergeSort();
question42_linearSearch();
return 0;
}Recursion and Math (Q43-Q50)
Recursion questions test ability to think recursively and solve problems using divide-and-conquer approaches [web:352][web:354]. These final 8 questions cover factorial, Fibonacci, GCD, power function, palindrome recursion, tower of Hanoi, prime checking, and sum of digits.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
// ============================================
// Q43: Factorial using recursion.
// ============================================
int factorial(int n) {
if (n == 0 || n == 1) {
return 1;
}
return n * factorial(n - 1);
}
void question43_factorial() {
printf("Q43: Factorial (Recursive)\n");
int n = 5;
printf("Factorial of %d: %d\n", n, factorial(n));
printf("Time: O(n), Space: O(n) recursion stack\n\n");
}
// ============================================
// Q44: Fibonacci series (recursive vs iterative).
// ============================================
int fibonacciRecursive(int n) {
if (n <= 1) return n;
return fibonacciRecursive(n - 1) + fibonacciRecursive(n - 2);
}
int fibonacciIterative(int n) {
if (n <= 1) return n;
int prev = 0, curr = 1;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
int temp = curr;
curr = prev + curr;
prev = temp;
}
return curr;
}
void question44_fibonacci() {
printf("Q44: Fibonacci Series\n");
printf("First 10 numbers (iterative): ");
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
printf("%d ", fibonacciIterative(i));
}
printf("\nRecursive fib(6): %d\n", fibonacciRecursive(6));
printf("Recursive: O(2^n), Iterative: O(n)\n\n");
}
// ============================================
// Q45: GCD using Euclidean algorithm (recursive).
// ============================================
int gcd(int a, int b) {
if (b == 0) return a;
return gcd(b, a % b);
}
void question45_gcd() {
printf("Q45: GCD (Greatest Common Divisor)\n");
int a = 48, b = 18;
printf("GCD of %d and %d: %d\n", a, b, gcd(a, b));
printf("Time: O(log min(a,b))\n\n");
}
// ============================================
// Q46: Power function (x^n) - efficient O(log n).
// ============================================
int power(int base, int exp) {
if (exp == 0) return 1;
int half = power(base, exp / 2);
if (exp % 2 == 0) {
return half * half;
} else {
return base * half * half;
}
}
void question46_power() {
printf("Q46: Power Function (Efficient)\n");
int base = 2, exp = 10;
printf("%d^%d = %d\n", base, exp, power(base, exp));
printf("Time: O(log n) using divide-and-conquer\n\n");
}
// ============================================
// Q47: Check palindrome using recursion.
// ============================================
bool isPalindromeRecursive(char *str, int start, int end) {
if (start >= end) return true;
if (str[start] != str[end]) return false;
return isPalindromeRecursive(str, start + 1, end - 1);
}
void question47_palindromeRecursive() {
printf("Q47: Palindrome Check (Recursive)\n");
char *str1 = "racecar";
char *str2 = "hello";
int len1 = 7, len2 = 5;
printf("%s is %s\n", str1,
isPalindromeRecursive(str1, 0, len1 - 1) ? "palindrome" : "not palindrome");
printf("%s is %s\n\n", str2,
isPalindromeRecursive(str2, 0, len2 - 1) ? "palindrome" : "not palindrome");
}
// ============================================
// Q48: Tower of Hanoi.
// ============================================
void towerOfHanoi(int n, char from, char to, char aux) {
if (n == 1) {
printf("Move disk 1 from %c to %c\n", from, to);
return;
}
towerOfHanoi(n - 1, from, aux, to);
printf("Move disk %d from %c to %c\n", n, from, to);
towerOfHanoi(n - 1, aux, to, from);
}
void question48_towerOfHanoi() {
printf("Q48: Tower of Hanoi\n");
int n = 3;
printf("Solving for %d disks:\n", n);
towerOfHanoi(n, 'A', 'C', 'B');
printf("Time: O(2^n)\n\n");
}
// ============================================
// Q49: Check if number is prime.
// ============================================
bool isPrime(int n) {
if (n <= 1) return false;
if (n == 2) return true;
if (n % 2 == 0) return false;
for (int i = 3; i * i <= n; i += 2) {
if (n % i == 0) return false;
}
return true;
}
void question49_primeCheck() {
printf("Q49: Prime Number Check\n");
printf("Prime numbers up to 30: ");
for (int i = 2; i <= 30; i++) {
if (isPrime(i)) {
printf("%d ", i);
}
}
printf("\nTime: O(√n)\n\n");
}
// ============================================
// Q50: Sum of digits using recursion.
// ============================================
int sumOfDigits(int n) {
if (n == 0) return 0;
return (n % 10) + sumOfDigits(n / 10);
}
void question50_sumOfDigits() {
printf("Q50: Sum of Digits (Recursive)\n");
int n = 12345;
printf("Sum of digits of %d: %d\n", n, sumOfDigits(n));
printf("Time: O(log n) where n is the number\n\n");
}
int main() {
printf("=== C Interview Questions: Recursion & Math ===\n\n");
question43_factorial();
question44_fibonacci();
question45_gcd();
question46_power();
question47_palindromeRecursive();
question48_towerOfHanoi();
question49_primeCheck();
question50_sumOfDigits();
return 0;
}Interview Preparation Strategy
Effective interview preparation requires systematic study combining theory, hands-on coding practice, and understanding of common patterns. Focus on mastering fundamentals before advancing to complex problems, and always analyze both time and space complexity when discussing solutions [web:354][web:355].
- Master pointer fundamentals first: Understand declaration, dereferencing, pointer arithmetic, and memory allocation before tackling data structures [web:343][web:358]
- Practice coding by hand: Many interviews use whiteboards or shared documents without IDE assistance, so practice writing syntactically correct code without autocomplete [web:354]
- Explain while coding: Verbalize your thought process, discuss trade-offs between approaches, and justify design decisions as interviewers evaluate communication skills [web:355]
- Analyze complexity: Always discuss time and space complexity using Big O notation, showing understanding of algorithmic efficiency [web:352]
- Test your code: Walk through examples with different inputs, consider edge cases like null pointers, empty arrays, single elements, and large datasets [web:354]
- Study common patterns: Two pointers, sliding window, hash tables, recursion, divide and conquer, and dynamic programming appear repeatedly [web:352]
- Debug systematically: When code fails, use logical debugging with print statements or debugger rather than random changes [web:355]
- Optimize iteratively: Start with a brute force solution that works, then optimize after confirming correctness rather than trying to write perfect code immediately [web:354]
- Practice on coding platforms: Use LeetCode, HackerRank, GeeksforGeeks to solve problems daily, focusing on understanding patterns rather than memorizing solutions [web:352]
- Conduct mock interviews: Practice with peers or use platforms to simulate real interview pressure and timing constraints [web:355]
Conclusion
Mastering these 50 C programming interview questions with code examples provides comprehensive preparation covering all major topics interviewers assess: pointer fundamentals including null pointers, dangling pointers, void pointers, pointer to pointer, and pointer arithmetic with practical demonstrations of each concept [web:343][web:358]; dynamic memory management using malloc, calloc, realloc, and free with proper error checking and memory leak prevention strategies; string and array manipulation including reversal, palindrome checking, duplicate removal, rotation, and two-pointer techniques for efficient O(n) solutions [web:352][web:354]; data structure implementation from scratch including singly linked lists with insertion, deletion, reversal, loop detection using Floyd's algorithm, finding middle elements, stacks using arrays with push/pop/peek operations, queues using linked lists, and checking balanced parentheses; sorting and searching algorithms with complete implementations of binary search O(log n), bubble sort O(n²), selection sort O(n²), insertion sort O(n²), quick sort O(n log n) average, merge sort O(n log n) guaranteed, and linear search O(n) with time and space complexity analysis for each [web:352]; and recursion with mathematical problems including factorial, Fibonacci comparing recursive O(2^n) versus iterative O(n) approaches, GCD using Euclidean algorithm, efficient power function O(log n), Tower of Hanoi, prime number checking O(√n), and sum of digits.
Each question includes working code that compiles and runs, demonstrating not just theoretical knowledge but practical implementation skills interviewers value [web:354][web:355]. The examples cover common pitfalls like forgetting to check malloc return values for NULL, double-free errors, buffer overflows from unsafe string functions, off-by-one errors in loops, and memory leaks from lost pointer references. By systematically studying these 50 questions, writing the code by hand, testing with various inputs including edge cases, analyzing complexity, and practicing explanations, candidates build the deep understanding and problem-solving confidence needed to excel in C programming technical interviews at companies ranging from startups to FAANG organizations [web:352][web:359]. Consistent daily practice on coding platforms combined with reviewing fundamental concepts, understanding algorithm patterns, and conducting mock interviews provides the comprehensive preparation necessary for interview success in C programming roles.
$ share --platform
$ cat /comments/ (0)
$ cat /comments/
// No comments found. Be the first!